Whether in the cinema, on DVDs, when streaming series or watching TV – children, young people and parents frequently encounter the FSK age labels in their everyday media lives. Find out what’s behind the FSK ratings, how the ratings can help parents choose appropriate movies and protect young people from potentially inappropriate content in this article.
The FSK stands for “Voluntary Self-Regulation of the Film Industry.” It is a German institution concerned with the age rating of cinematic content on all distribution channels such as cinema, DVD/Blu-ray and streaming.
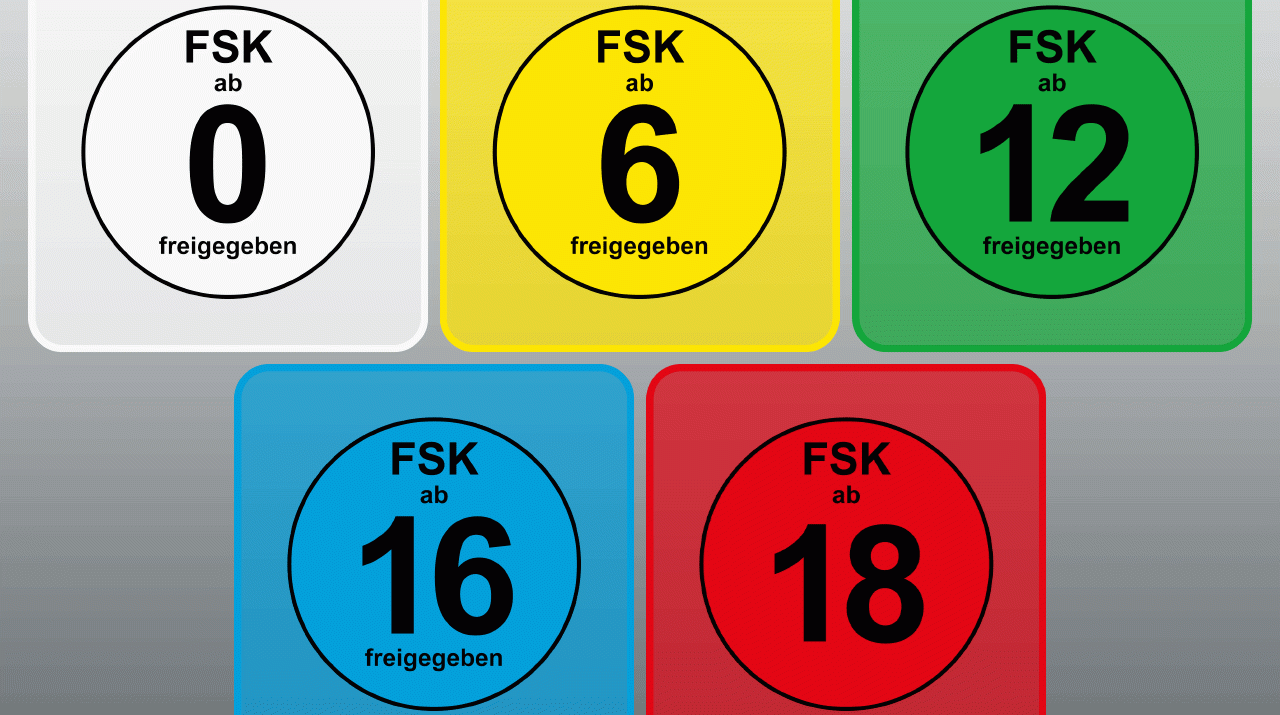
The FSK’s task is to classify and label movies and videos in an age-appropriate manner. In doing so, they examine the entire content and the portrayal of problematic aspects such as violence and sexuality. The labeling with an age rating takes the form of colored symbols such as “from 0” or “from 6”. The symbols can be found, for example, on packaging such as the DVD case or on movie posters.
The FSK ratings are based on the German Youth Protection Act (JuSchG). It contains legal provisions to protect children and young people from inappropriate content. The FSK is not a state institution, but a self-regulatory body of the film industry, which in Germany is supported by various interest groups under the umbrella of the umbrella organization of the film industry. However, state representatives are directly involved in the audits.
The FSK evaluates various media in the film and entertainment industry when a review is requested, in particular
Not all media are rated by the FSK. Computer games are checked by the Entertainment Software Self-Regulation Body (USK), while the Voluntary Self-Regulation Body for Television (FSF e.V.) is (also) responsible for television content and streaming services.
The age restrictions serve to protect minors in Germany and are based on the media competence attributed to different age groups of children and young people. Volunteer examiners from all over Germany work at the FSK. They come from different professional fields, e.g. journalism, media studies, education and justice.
The committee examinations take place at the FSK in Wiesbaden. After viewing the films and videos together, they discuss and vote on the age rating. The basis for the rating is the Youth Protection Act and the principles of the FSK. Consideration is given to plot, dialogue, character portrayal, visuals, specific themes such as violence and sexuality, and music.
Alternatively, after training, applicants can have their content rated using the FSK classification tool. The final decision on the test result is then made by the state representatives at the FSC. More information on the testing procedures can be found in the FSC’s principles and on the FSC website.
The following indications and problem areas have particular relevance for the respective release:
Since 2023, the FSK has been implementing a new provision in the German Protection of Minors Act and adding additional information to the known age ratings. These so-called “descriptors” are intended to explain the main reasons for the release and thus offer families more guidance when selecting films and series. More information can be found on the FSC website.
The FSK’s age ratings serve to protect minors, ensuring that children and young people are not adversely affected by content that is unsuitable for them. The releases are binding, which means, for example: films from the age of 12 may only be viewed by younger children in the cinema when accompanied by an adult.
The state does not determine what movies children can watch at home. Parents can also make media accessible to their children that are not approved for their age. In doing so, they must not neglect their duty to educate: